Job Submission and Management (HPC Phase III)
In the HPC Phase III(ACD) platform, jobs can be submitted to the cluster through the Slurm scheduler, and resources are allocated and scheduled for calculation according to certain rules.
For more information on the usage of Slurm commands, please refer to the official documentation: Slurm Documentation
Job Submission
Submitting a Regular Job (Command Line Mode)
Users can submit a job using the sbatch <params> <job_name> command and specify the parameters.
$sbatch -p acd_u --input=input.sh -o output_%j.txt -e err_%j.txt -n 8 --gres=gpu:1 job_script.sh
Common params
-p acd_u: Specify the acd_u partition. For full partition information, please check: Cluster partitions
--input input.sh: Specify the job input file
-o output_%j.txt: Specify the standard output file of the job, where %j is the job number
-e err_%j.txt: Specify the standard error output file of the job
-n 8: Specify the total number of CPU cores
--gres 1: Specify the number of GPU cards
-w ACD1-1,ACD1-2: Specify the ACD1-1 and ACD1-2 nodes. Use thesinfocommand to view node information
-x "~ACD1-1": Exclude the ACD1-1 node
-D /apps: Specify the job execution path as /apps; by default, without the -D option, the job execution path is the job submission path
Submitting a Regular Job (Script Mode)
In addition to command line submission, users can submit jobs through the script submission mode, which is convenient for users to manage job submission parameters and related job parameter configurations. Write the parameters that need to be specified during submission into the script, and users can reuse the script in batches without having to specify the parameters each time.
Script submission: sbatch ``my_job.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p acd_u # Specify the GPU partition
#SBATCH -o output_%j.txt # Specify the standard output file of the job, where %j is the job number
#SBATCH -e err_%j.txt # Specify the standard error output file of the job
#SBATCH -n 8 # Specify the total number of CPU cores
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:1 # Specify the number of GPU cards
#SBATCH -D /apps # Specify the job execution path as /apps
# The following are the commands to be executed by the job
echo "Job started at $(date)"
python your_script.py # Assume running a Python script
echo "Job ended at $(date)"
Submit parallel jobs
Users can submit multi-node parallel jobs.
Script submission: sbatch ``my_job.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p acd
#SBATCH --job-name=speed_test
#SBATCH -o /data/user/user11/project/PRM2/slurm_log/%j.out # slurm的输出文件,%j是jobid
#SBATCH --nodes=2 # 请求2个节点
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=4 #每个节点上4个任务
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4 # 每个节点4个GPU
module load anaconda3
module load cuda/12.4
export NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=vlan0.2135
export NCCL_NET_GDR_LEVEL=PHB
export NCCL_IB_DISABLE=0
export NCCL_IB_HCA=mlx5_0,mlx5_1,mlx5_2,mlx5_6,mlx5_7,mlx5_8,mlx5_9,mlx5_10
export NCCL_IB_GID_INDEX=3
export NCCL_IB_TC=138
export NCCL_NSOCKS_PERTHREAD=8
export NCCL_SOCKET_NTHREADS=4
export NCCL_NVLS_ENABLE=0
export NCCL_NVLS_PLUGIN=1
export NCCL_NVLS_LANES=2
export NCCL_IB_QPS_PER_CONNECTION=8
export NCCL_IB_SPLIT_DATA_ON_QPS=1
export NCCL_MIN_CTAS=32
export NCCL_MAX_CTAS=128
export NCCL_IB_RETRY_CNT=7
export NCCL_MIN_NCHANNELS=64
export NCCL_MAX_NCHANNELS=256
export NCCL_NCHANNELS_PER_NET_PEER=32
export NCCL_BUFFSIZE=33554432
export NCCL_LL_BUFFSIZE=33554432
export NCCL_P2P_NET_CHUNKSIZE=2097152
export NCCL_P2P_LEVEL=nvl
export NCCL_ALGO=nvlstree,ring
export NCCL_LL_MAX_NCHANNELS=4
export NCCL_CROSS_NIC=1
export NCCL_IGNORE_CPU_AFFINITY=1
export NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=0
export NCCL_COLLNET_ENABLE=1
export NCCL_DEBUG=INFO
export NCCL_TIMEOUT=3600
export NCCL_IB_TIMEOUT=3600
echo "Job started at $(date)"
python your_script.py # Assume running a Python script
echo "Job ended at $(date)"
Submitting an Array Job
Users can submit array jobs to share the same executable file and resource requirements, but with different input and output files.
Script submission: sbatch ``my_job.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -p normal # Specify the partition
#SBATCH -o output_%A_%a.txt # Specify the standard output file, where %A is the main job ID of the array job, and %a is the index of the current sub-job
#SBATCH -e error_%A_%a.txt # Specify the standard error output file
#SBATCH -n 1 # Specify the number of CPU cores required for each sub-job
#SBATCH --array=1-10 # Specify the range of the array job, here it means 10 sub-jobs from 1 to 10
# Set different parameters according to the sub-job index
PARAM=$SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID
# Execute the job command, here taking printing the parameter as an example
echo "Running task $PARAM"
python your_script.py $PARAM # Assume running a Python script and passing in the parameter
Parameter Description:
#SBATCH --array=1-10: This instruction defines the range of the array job. 1-10 means that 10 sub-jobs will be created, and the sub-job indices range from 1 to 10. You can also use commas to separate different index values, such as --array=1,3,5, which means only creating sub-jobs with indices 1, 3, and 5; you can also use a step size, such as --array=1-10:2, which means sub-jobs with indices 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9.
$SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID: This is an environment variable. In each sub-job, its value is equal to the index of the sub-job. You can set different parameters or input files according to this index.
%A and %a: In the naming of the output file, %A represents the main job ID of the array job, and %a represents the index of the current sub-job. This ensures that the output files of each sub-job will not overwrite each other.
Submitting an Interactive Job
An interactive job is a kind of front-end-like job. Although the job is executed on the back-end (a certain computing node), the execution process and output will be presented in real-time to the user submission end, and during this process, the user can also participate and carry out necessary human-computer interaction.
Users can submit an interactive job using srun
$ srun -p acd_u -n 4 --mem=8G --gres=gpu:1 --time=01:00:00 --pty bash
Parameter Description:
--time=01:00:00: Set the maximum running time of the job to 1 hour. When this time limit is reached, the job will be automatically terminated.
-pty bash: Allocate a pseudo-terminal and start the bash shell
All jobs have a default maximum running time of 7 days. Before the expiration, you can submit an IT work order on HKUST(GZ) Go to apply for an extension of 7 days.
Job Viewing and Management (Command Line)
Viewing User Jobs (Pending, Running, Suspended)
$ spartition -u <username> [-t PENDING,RUNNING,SUSPENDED]
Viewing User's Historical Jobs
$ sacct -u <username> [--array]
Viewing Job Details
$ scontrol show job <jobid>
Viewing Array Jobs
$ scontrol show job <jobid_$task_id>
Viewing the Reason for a Job Being PENDING
$ scontrol show job <jobid>
Suspending a Job
$ scontrol suspend <jobid>
Resuming a Job
$ scontrol resume <jobid>
Terminating a Job
$ scancel <jobid>
Job Viewing and Management (WEB)
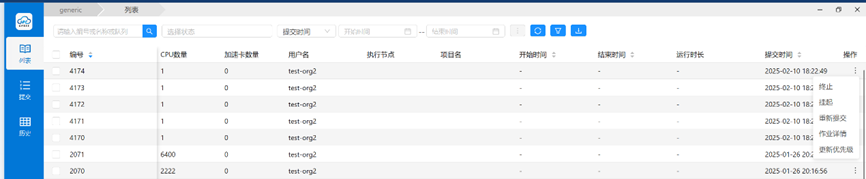
View User Jobs
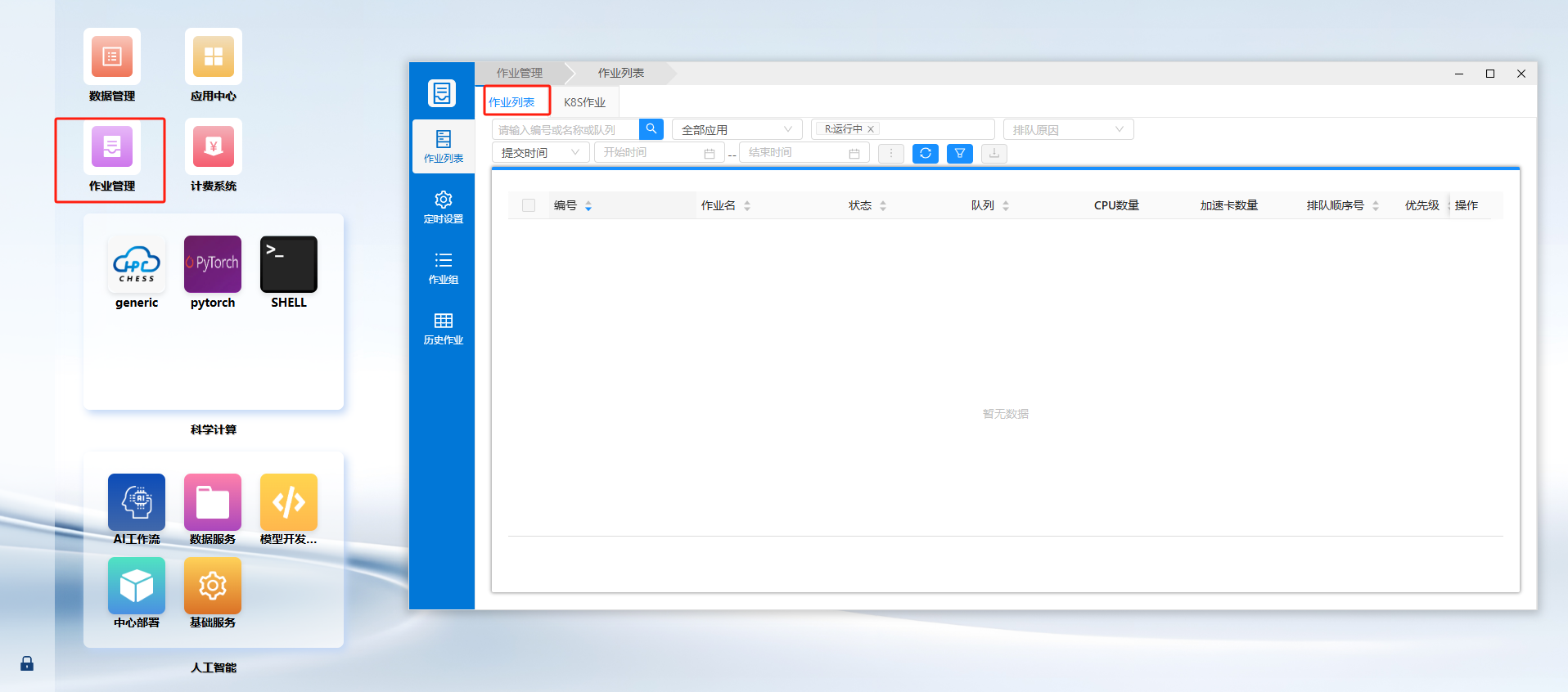
Log in to the HPC Phase III Platform Portal --- Job Management --- Job List.
Historical jobs display the status of jobs that have ended more than seven days ago.
View Job Details
Click on the job name to view the details of the corresponding job. Switch between: Output, Data, Monitoring, Details, and Performance to view the corresponding information.
For running jobs, click "Performance" to view the resource usage status of the job on that node, such as memory, CPU, and accelerator cards.
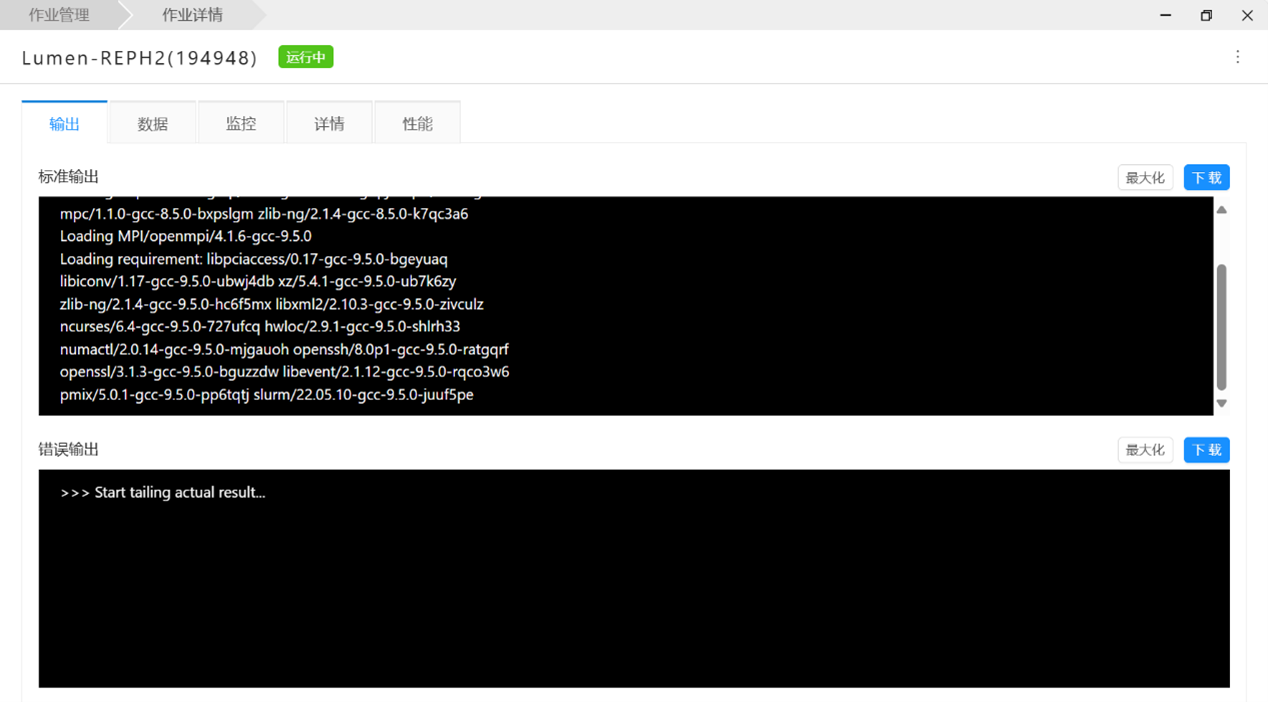

Terminate Jobs
Select the corresponding job and perform the termination operation in the rightmost [Operation] column.